Neurology is a fascinating branch of medicine focusing on diagnosing and treating disorders of the nervous system. Whether you’re considering a career in neurology or just starting your neurology rotation, this guide aims to provide you with practical information. While not everyone will pursue neurology, understanding how to assess patients with neurological issues, identify the affected areas in the nervous system, manage common neurological conditions, and know when to seek help from neurologists is important across medical specialties.
What is Neurology Rotation?
In the United States, there are currently over 3,597 employed neurologists. A neurology rotation is a period of time during medical training (typically 4 to 8 weeks), undertaken in medical school or residency. As part of the clerkship, students or trainees spend a designated amount of time working in the field of neurology. During this rotation, students have the opportunity to gain hands-on experience in evaluating and managing patients with neurological disorders under the supervision of experienced neurologists. This may involve working in both inpatient and outpatient settings, conducting neurological examinations, interpreting diagnostic tests, and participating in treatment planning. It helps provide exposure to various neurological conditions and helps students and trainees develop essential clinical skills in this specialized area of medicine.
When Should I Start Applying for a Neurology Rotation?
The placement of your neurology rotation within your medical training depends on your interest in pursuing it as a specialty. If neurology is the field you’re considering, it’s advisable not to schedule this rotation at the end of your training. Instead, consider placing it as the second or third rotation out of the total of four quarters in the year.
This way, you will be able to gain foundational experience before diving into rotations of higher interest. By having exposure to neurology earlier in your training, you’ll have ample time to develop essential skills and knowledge that can be applied to subsequent rotations. Additionally, scheduling neurology earlier also allows you to obtain valuable references for residency program applications. Moreover, you will also be able to better judge if neurology aligns with your career aspirations through firsthand experience during your rotation
Making The Most of Your Neurology Rotation
During your neurology rotation, you’ll engage in a mix of outpatient and inpatient experiences. Similar to internal medicine, expect rounds that demand thorough preparation and active participation, serving as key learning opportunities
Inpatient Service
In the inpatient setting, you’ll encounter patients with more severe neurological cases. These include seizures, demyelinating neuropathies, inflammatory neuropathies, etc. An essential skill in neurology is promptly diagnosing the location of lesions within the nervous system. Familiarize yourself with neurologic injury locations before rounds to impress attending physicians.
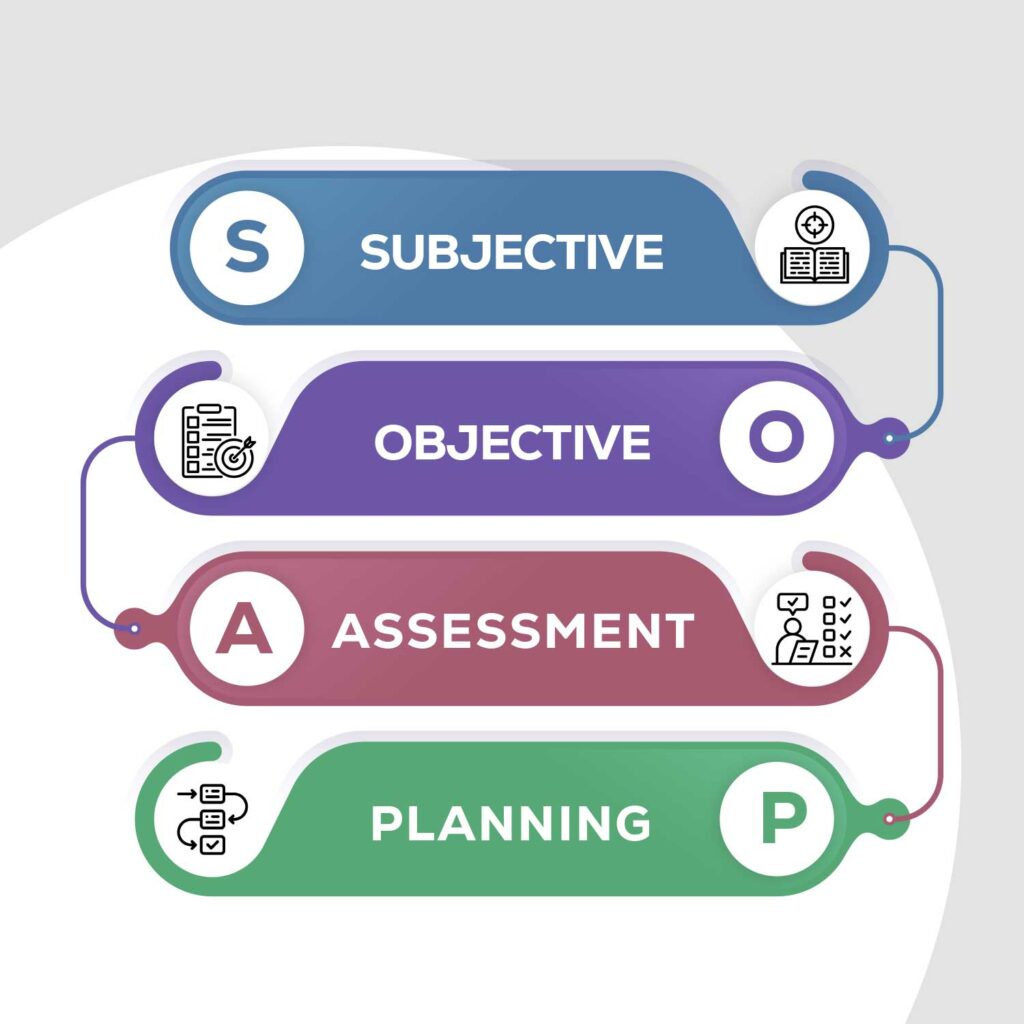
During rounds, adhere to the SOAP method:
- Subjective: Obtain a comprehensive medical history from the patient.
- Objective: Perform a thorough clinical examination and report your findings.
- Assessment: Present your diagnosis and differential diagnosis (DDx).
- Planning: Develop a management plan for the patient’s care.
For instance, if presented with a patient who recently suffered a seizure, gather a detailed medical history. Then objectively assess neurological deficits, and present your diagnosis and differential diagnosis. You should also propose further care steps, such as scheduling imaging appointments and initiating appropriate medications under supervision.
Outpatient Service
During your neurology rotation, the outpatient clinic offers two main focuses. Firstly, you’ll gain insight into the initial steps of patient admission. This is an essential skill for Shelf exams. Emphasis is placed on understanding common pathologies like Alzheimer’s, rather than rarer conditions such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. On top of that, it also provides an opportunity to learn about continuity of care. This includes adjusting treatment plans, such as introducing COMT or MAO inhibitors for Parkinson’s patients experiencing on-off phenomena. Overall, the rotation will enhance your clinical skills, diagnostic capabilities, and ability to manage a variety of neurological disorders across different clinical settings
Most Common Neurology Conditions
| No. | Condition | Explanation |
| 1. | Stroke | A cerebrovascular event resulting in the interruption of blood flow to the brain, leading to neurological deficits. |
| 2. | Epilepsy | A chronic neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain. |
| 3. | Alzheimer’s Disease | A progressive neurodegenerative disorder resulting in memory loss, cognitive decline, and behavioral changes. |
| 4. | Parkinson’s Disease | A neurodegenerative disorder affecting movement, characterized by tremors, stiffness, and impaired balance. |
| 5. | Migraine | Recurrent headaches are often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound. |
| 6. | Multiple Sclerosis | An autoimmune disease causing damage to the myelin sheath, leading to neurological symptoms such as weakness, numbness, and visual disturbances. |
| 7. | Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) | Damage to the brain is caused by an external force, resulting in cognitive, physical, and emotional impairments. |
| 8. | Neuropathy | Damage or dysfunction of peripheral nerves leads to symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness. |
| 9. | Seizures | Abnormal electrical activity in the brain results in temporary disturbances in behavior, consciousness, or sensation. |
| 10. | Brain Tumors | Abnormal growths of tissue within the brain can cause a variety of neurological symptoms depending on their location and size. |
How to Prepare for the Neurology Clerkship?

To prepare technically, consider utilizing various resources such as neurology rotation books, online modules, and practice questions. Textbooks like Adams and Victor’s Principles of Neurology provide comprehensive coverage of essential neurology topics. Additionally, online platforms like AMBOSS offer tailored study materials, including interactive case simulations and video lectures. Moreover, incorporating practice questions into your study routine also helps reinforce key concepts and assess your understanding.
Don’t forget to practice clinical skills relevant to neurology, such as neurological examinations and diagnostic test interpretation. Staying organized with a structured study schedule ensures thorough coverage of all necessary topics. Finally, staying updated with recent developments in neurology through medical journals and conferences enhances your knowledge base.
How to Clear the Neurology Shelf Exam?
Preparing for the Neurology Shelf Exam requires a balanced approach, combining hospital-based activities and home study routines. Here is some effective neurology rotation advice:
- Firstly, upon encountering a patient, focus on obtaining a detailed medical history and conducting a thorough physical examination to orient your diagnosis. Later, at home, target specific pathologies using resources like Blueprints. Develop your own treatment plan and compare it with the one chosen by the resident or attending physician.
- Alternatively, if there’s flexibility in patient selection, choose cases related to recently studied pathologies. Familiarize yourself with the clinical findings specific to the patient and the disease to reinforce your understanding and application of the studied material.
For success in the exam, consider these tips:
- Initially skim through questions, answering easy ones and marking unsure ones for review during breaks.
- Take mental breaks to avoid rushing and making errors.
- For unanswered questions, select the most probable choice or the one you believe the test makers expect.
- Begin using question banks early, benefiting from the hypercorrection effect when faced with unknown content.
Utilize resources like the NBME Clinical Mastery series for comprehensive assessment towards the end of your rotation.
FAQs – Neurology Rotation
Neurology rotations typically last between 4 to 8 weeks, although the duration may vary depending on your institution’s curriculum and scheduling.
Neurology way rotations can provide valuable exposure to different healthcare systems, patient populations, and academic environments. However, they are not mandatory for neurology residency applications. Consider pursuing away rotations if you want to explore specific programs or geographic locations.
Subspecialties such as interventional neurology, neurocritical care, and neuromuscular medicine tend to offer higher earning potential compared to general neurology practice. Factors such as location, experience, and practice setting also influence earning potential.
To succeed in your neurology rotation, approach each patient encounter with curiosity, empathy, and attention to detail. Actively participate in rounds, seek feedback from faculty, and take initiative in learning opportunities. Developing strong communication skills and clinical reasoning abilities will set you apart as a standout student. Make good use of neurology rotation resources and neurology clerkship books
A career in neurology offers intellectually stimulating work, opportunities for professional growth, and meaningful patient interactions. Neurologists play a vital role in diagnosing and managing complex neurological conditions, contributing to research advancements, and enhancing patient outcomes. The field’s interdisciplinary nature and continuous learning potential make it an appealing and fulfilling career option.



